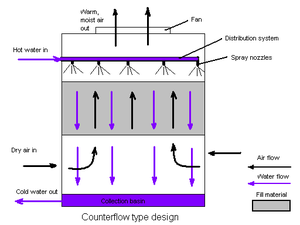
Cooling Towers
A Cooling Tower is a heat rejection device, which extracts waste heat to the atmosphere though the cooling of a water stream to a lower temperature. The type of heat rejection in a cooling tower is termed evaporative in that it allows a small portion of the water being cooled to evaporate into a moving air stream to provide significant cooling to the rest of that water stream.
Otherwise simply we can say Cooling towers are heat removal devices used to transfer process waste heat to theatmosphere. Cooling towers may either use the evaporation of water to remove process heat and cool the working fluid to near the wet-bulb air temperature or, in the case of closed circuit dry cooling towers, rely solely on air to cool the working fluid to near the dry-bulb air temperature.
Common applications include cooling the circulating water used in oil refineries,petrochemical and other chemical plants, thermal power stations and HVACsystems for cooling buildings.
Cooling towers vary in size from small roof-top units to very large hyperboloid structures that can be up to 200 metres tall and 100 metres in diameter, or rectangular structures that can be over 40 metres tall and 80 metres long. The hyperboloid cooling towers are often associated with nuclear power plants, although they are also used to some extent in some large chemical and other industrial plants. Although these large towers are very prominent, the vast majority of cooling towers are much smaller, including many units installed on or near buildings to discharge heat from air conditioning.
Industrial cooling towers can be used to remove heat from various sources such as machinery or heated process material. The primary use of large, industrial cooling towers is to remove the heat absorbed in the circulating cooling water systems used in power plants, petroleum refineries, petrochemical plants, natural gas processing plants, food processing plants, semi-conductor plants, and for other industrial facilities such as in condensers of distillation columns, for cooling liquid in crystallization, etc.