Difference between revisions of "Mixers"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (10 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Mixing]]{{Knoppen}} | [[Category:Mixing]]{{Knoppen}} | ||
<noinclude><!------------------------------------------------ | <noinclude><!------------------------------------------------ | ||
| Line 8: | Line 7: | ||
* Please start editing this page after the /noinclude | * Please start editing this page after the /noinclude | ||
* -------------------------------------------------></noinclude> | * -------------------------------------------------></noinclude> | ||
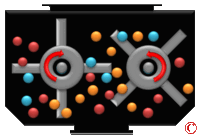
[[Image:Paddle-Mixers-Logo.gif|thumb|200px| | [[Image:Paddle-Mixers-Logo.gif|thumb|200px|Paddle Mixer]] | ||
[[Image:V-Blender-Logo.gif|thumb|200px| | [[Image:V-Blender-Logo.gif|thumb|200px|V Blender]] | ||
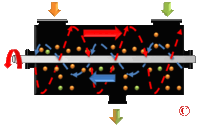
[[Image:Ribbon-Blender-Logo.gif|thumb|200px| | [[Image:Ribbon-Blender-Logo.gif|thumb|200px|Ribbon Blender.]] | ||
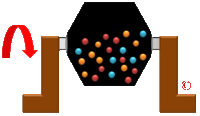
[[Image:Double-Cone-Blender-Logo.gif|thumb|200px| | [[Image:Double-Cone-Blender-Logo.gif|thumb|200px|Double Cone Blender]] | ||
[[Image:High-Shear-Mixers-Granulators-Logo.gif|thumb|200px| | [[Image:High-Shear-Mixers-Granulators-Logo.gif|thumb|200px|High shear Mixer/Granulator]] | ||
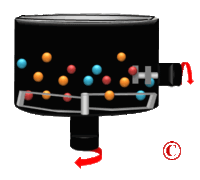
[[Image:Drum-Blender-Logo.gif|thumb|200px|Drum-Blender]] | [[Image:Drum-Blender-Logo.gif|thumb|200px|Drum-Blender]] | ||
'''Mixers ''' are used to mix or blend a wide range of materials used in different industries including the food, chemical, pharmaceutical, plastic and mineral industries. They are mainly used to mix different materials using different types of blades to make a good quality homogeneous mixture. Included are dry blending devices, paste mixing designs for high viscosity products and high shear models for emulsification, particle size reduction and homogenization. | '''Mixers ''' are used to mix or blend a wide range of materials used in different industries including the food, chemical, pharmaceutical, plastic and mineral industries. They are mainly used to mix different materials using different types of blades to make a good quality homogeneous mixture. Included are dry blending devices, paste mixing designs for high viscosity products and high shear models for emulsification, particle size reduction and homogenization. | ||
Mixers range from laboratory to production line scale, including: | |||
* [[Ribbon Blenders]] | |||
* [[V-Type Blenders]] | |||
* [[Cone Screw Blenders]] | |||
* [[Screw Blenders]] | |||
* [[Double Cone Blenders]] | |||
* [[Double Planetary Mixers]] | |||
* [[Contra Rotating Mixers]] | |||
* [[Double Shaft Mixers]] | |||
* [[Triple Shaft Mixers]] | |||
* [[Vacuum Mixers]] | |||
* [[Planetary Dispersers]] | |||
* [[High Shear Mixers]] | |||
* [[Dispersion Mixers]] | |||
* [[Paddle Mixers]] | |||
* [[Jet Mixers]] | |||
* [[Mobile Mixers]] | |||
* [[Drum Blenders]] | |||
* [[Banbury Mixers]] are effective at mixing or kneading viscous materials. They can operate at different temperatures and pressures for mixing different solutions and can also have internal or external heating systems added to them. | |||
==Options== | |||
== | * Spray nozzles | ||
* CIP | |||
* PLC | |||
* Pneumatic or electric systems | |||
* Hydraulic or electronic soft start mechanisms so that they start and stop smoothly | |||
== Video == | == Video == | ||
<youtube>q36ex3Bp3K8</youtube> | <youtube>q36ex3Bp3K8</youtube> | ||
Latest revision as of 01:19, 21 August 2012
Mixers are used to mix or blend a wide range of materials used in different industries including the food, chemical, pharmaceutical, plastic and mineral industries. They are mainly used to mix different materials using different types of blades to make a good quality homogeneous mixture. Included are dry blending devices, paste mixing designs for high viscosity products and high shear models for emulsification, particle size reduction and homogenization.
Mixers range from laboratory to production line scale, including:
- Ribbon Blenders
- V-Type Blenders
- Cone Screw Blenders
- Screw Blenders
- Double Cone Blenders
- Double Planetary Mixers
- Contra Rotating Mixers
- Double Shaft Mixers
- Triple Shaft Mixers
- Vacuum Mixers
- Planetary Dispersers
- High Shear Mixers
- Dispersion Mixers
- Paddle Mixers
- Jet Mixers
- Mobile Mixers
- Drum Blenders
- Banbury Mixers are effective at mixing or kneading viscous materials. They can operate at different temperatures and pressures for mixing different solutions and can also have internal or external heating systems added to them.
Options
- Spray nozzles
- CIP
- PLC
- Pneumatic or electric systems
- Hydraulic or electronic soft start mechanisms so that they start and stop smoothly
Video