Difference between revisions of "Twin Tower Dryers"
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
* Please start editing this page after the /noinclude | * Please start editing this page after the /noinclude | ||
* -------------------------------------------------></noinclude> | * -------------------------------------------------></noinclude> | ||
[[File:Twin_Tower_Dryers.jpg|thumb|200px|right|Twin Tower Dryers]] | |||
[[File:Twin_Tower_Dryers_Principle.jpg|thumb|200px|right|Twin Tower Dryer Principle]] | |||
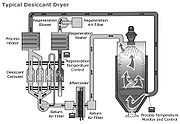
The '''Twin Tower Dryers''' are used for drying air in storage tanks or pneumatic systems and are beneficial in the drying of hygroscopic (water-absorbing) resins. These dryers remove water from the air by passing it through a desiccant that absorbs moisture. | The '''Twin Tower Dryers''' are used for drying air in storage tanks or pneumatic systems and are beneficial in the drying of hygroscopic (water-absorbing) resins. These dryers remove water from the air by passing it through a desiccant that absorbs moisture. | ||
==Features== | ==Features== | ||
The Twin Tower Dryers consist mainly of two cylinders containing desiccant, connected by a valve system. | The Twin Tower Dryers consist mainly of two cylinders containing desiccant, connected by a valve system. | ||
==Operation== | ==Operation== | ||
When the desiccant in the first cylinder is saturated, the air flow can be switched to the cylinder containing the dried desiccant. | When the desiccant in the first cylinder is saturated, the air flow can be switched to the cylinder containing the dried desiccant. | ||
==Dessicant Types== | ==Dessicant Types== | ||
Common desiccants are silica gel (an oxide of silica), alumina (aluminum oxide) and calcium sulfate (the anhydrous form of gypsum). | Common desiccants are silica gel (an oxide of silica), alumina (aluminum oxide) and calcium sulfate (the anhydrous form of gypsum). | ||
==Types of Dryers== | ==Types of Dryers== | ||
While manual desiccant dryers exist, many dryers are Twin Tower Dryers, as noted in the Plant Services magazine article, "The Economics of Operating Twin Tower Dryers," by Noel Corral and Andrew | While manual desiccant dryers exist, many dryers are Twin Tower Dryers, as noted in the Plant Services magazine article, "The Economics of Operating Twin Tower Dryers," by Noel Corral and Andrew Sheaffer. | ||
==Most Expensive== | ==Most Expensive== | ||
Heatless Twin Tower Dryers run a portion of dried compressed air through the previously utilized cylinder to extract moisture from its desiccant. | Heatless Twin Tower Dryers run a portion of dried compressed air through the previously utilized cylinder to extract moisture from its desiccant. | ||
==Least Expensive== | ==Least Expensive== | ||
Heated purge Twin Tower Dryers use less air than the heatless variety in addition to heat, which helps the air carry away more water as it passes through the saturated desiccant.==Best Compromise==Heated blower purge regenerative Twin Tower Dryers use air from outside the dryer that is heated and sent through the water-saturated desiccant for drying. | Heated purge Twin Tower Dryers use less air than the heatless variety in addition to heat, which helps the air carry away more water as it passes through the saturated desiccant. | ||
==Best Compromise== | |||
Heated blower purge regenerative Twin Tower Dryers use air from outside the dryer that is heated and sent through the water-saturated desiccant for drying. | |||
==Classification== | ==Classification== | ||
| Line 31: | Line 44: | ||
* Compact Heatless Twin Tower Dryer | * Compact Heatless Twin Tower Dryer | ||
* Mini Heatless Twin Tower Dryer | * Mini Heatless Twin Tower Dryer | ||
Revision as of 09:18, 30 July 2012
The Twin Tower Dryers are used for drying air in storage tanks or pneumatic systems and are beneficial in the drying of hygroscopic (water-absorbing) resins. These dryers remove water from the air by passing it through a desiccant that absorbs moisture.
Features
The Twin Tower Dryers consist mainly of two cylinders containing desiccant, connected by a valve system.
Operation
When the desiccant in the first cylinder is saturated, the air flow can be switched to the cylinder containing the dried desiccant.
Dessicant Types
Common desiccants are silica gel (an oxide of silica), alumina (aluminum oxide) and calcium sulfate (the anhydrous form of gypsum).
Types of Dryers
While manual desiccant dryers exist, many dryers are Twin Tower Dryers, as noted in the Plant Services magazine article, "The Economics of Operating Twin Tower Dryers," by Noel Corral and Andrew Sheaffer.
Most Expensive
Heatless Twin Tower Dryers run a portion of dried compressed air through the previously utilized cylinder to extract moisture from its desiccant.
Least Expensive
Heated purge Twin Tower Dryers use less air than the heatless variety in addition to heat, which helps the air carry away more water as it passes through the saturated desiccant.
Best Compromise
Heated blower purge regenerative Twin Tower Dryers use air from outside the dryer that is heated and sent through the water-saturated desiccant for drying.
Classification
There are different types of Twin Tower Dryers. These are:
- Small Heatless Twin Tower Dryer
- Large Heatless Twin Tower Dryer
- Compact Heatless Twin Tower Dryer
- Mini Heatless Twin Tower Dryer